

The multilingual native mobile application lets users experience the power of IPTrack on the go and is available for smartphones and tablets. Do not miss important messages from the system. iptrace -a -s 193.0.0.1 -i en0 network.log, All TCP/IP packets that originate from host. Alongside with receiving and viewing notifications, create new notifications, edit the already existing ones and view the notifications history. Automatic login information for the ftp and rexec commands. Generate reports by selecting the unit, report template, time interval, and get analytics right where you are at the moment. Monitor the unit’s exact location and all the parameters received from it. TRACEROUTE sends the first echo packet to the local router and then increments the TTL by reaching the destination router. Note! You can search for units directly on the map with the help of the search field. How Traceroutes (TRACERT) Works As we have seen above, Traceroutes is a command-line utility used to check the route of a packet while reaching its destination. Access units, geofences, tracks and event markers on the map with the option to detect your own location. Next time just use rpm -ql iptraf-ng to list the package contents. Send commands to unit groups and search by groups’ titles. The binary of the iptraf-ng package is iptraf-ng. Get all the necessary information on movement and ignition state, data actuality, and unit location in real time. It offers both basic and advanced functionality of the desktop version in a user-friendly mobile interface. You should now be able to use the tracert command and understand its output.With the mobile IPTrack app, maintain access to IPTrack GPS tracking platform anytime, anywhere. If this isn’t available, only the IP address of the router is displayed. Some run under AIX, others run on dedicated hardware. There are many tools for observing the activity, both normal and pathological, on the network. Domain Name : The domain name, if available, can often help you see the location of a router. Using iptrace to Analyze Performance Problems. After running a traceroute command, the results displayed are a list of the hops that data packets take along their path to the designated IP address or.

If you see a * in some columns, you didn’t receive a response – which could indicate packet loss. Traceroute sends three packets to each hop and displays each time, so you have some idea of how consistent (or inconsistent) the latency is. You can check your IP from what is my IP address. If you want to traceroute a domain, enter a domain, or if you want to traceroute an IP, enter an IP in the provided space and click the 'Trace Route' button.
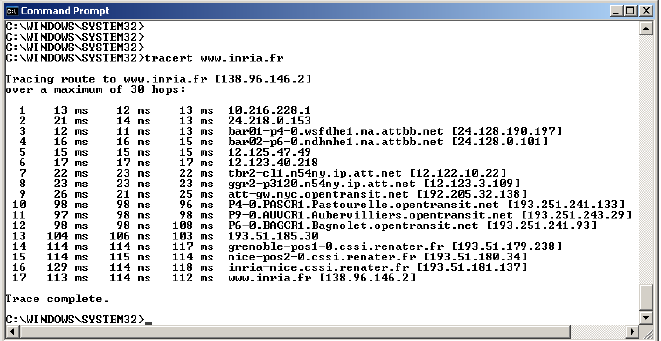
This is often referred to as latency, and is the same number you see when using ping. To Traceroute an IP address or domain, perform the following steps. RTT1, RTT2, RTT3: This is the round-trip time that it takes for a packet to get to a hop and back to your computer (in milliseconds).Hop: Whenever a packet is passed between a router, this is referred to as a “hop.” For example, in the output above, we can see that it takes 14 hops to reach How-To Geek’s servers from my current location.The first line represents your home router (assuming you’re behind a router), the next lines represent your ISP, and each line further down represents a router that’s further away. The iptrace command can be very useful to find out what network traffic flows to and from an AIX system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
